Introduction
A recent study by the American Medical Association found that 85% of physicians now see telemedicine as a long-term part of their practice. This statistic resonates with my own experience and is something I am grateful for—last week, I avoided more than four hours of stressful highway driving when my kids’ specialist encouraged us to meet virtually instead of in-person. This saved me money and gas, and I didn’t have to take any time off work. The kids missed less school, and the doctor was able to see more patients.
Telemedicine is reshaping the medical landscape, offering unique advantages for patients and doctors. Doctors are redefining their professional boundaries and gaining access to cutting-edge technological tools for their practice. They are finding ways to benefit financially from new economic models while still serving their patients well, and they are being presented with opportunities for professional growth. Finally, while there are numerous benefits of telemedicine for doctors, it does present ethical challenges that need further exploration.
Table of Contents
- Redefining Professional Boundaries
- Technological Empowerment
- Economic Paradigm Shift
- Ethical Considerations and Professional Growth
Redefining Professional Boundaries
According to a Kaiser Family Foundation report, in the last quarter of 2023, over 12.6% of Medicare beneficiaries received a telehealth service, indicating a sustained higher level of telehealth utilization compared to pre-pandemic levels. Telemedicine is becoming more commonly used, and as it trends in that direction, the traditional doctor-patient relationship is evolving. Fortunately, as professional boundaries are redefined, doctors and patients are experiencing the benefits of telemedicine.
Telemedicine Expands Work-Life Integration Opportunities for Doctors
There are several benefits of telemedicine for doctors, including the option to easily schedule and customize their availability. Some doctors find it less disruptive to schedule weekend and evening appointments around their personal lives, leading to a better work-life balance and increased job satisfaction. Jeff Drasnin, M.D. of ESD Pediatric Group in Milford, Ohio, uses an athenahealth product and happily reports, “I am home for dinner every night.” Interestingly, pediatrics as a specialty conducts the highest number of weekend appointments virtually, highlighting the benefit of increased convenience for providers and families. To read more about that benefit and how telemedicine is reshaping healthcare delivery, check out our article on the top 8 advantages and disadvantages of telemedicine in 2025.
Many software providers, such as Coviu, tout reduced paperwork and automated administrative tasks as benefits of telemedicine for doctors. Obtaining prior authorizations, dealing with claims, and tracking coding changes are just three examples of tasks that take away from patient care and often result in frustration for doctors who would prefer to practice medicine rather than do paperwork.
Digital Nomad Doctors
An emerging trend among doctors is the concept of digital nomadism—practicing medicine remotely while traveling. Whether in pursuit of language, culture, or the sheer joy of traveling, many physicians are drawn to this possibility and believe it will provide both personal growth and a greater perspective on healthcare. Telemedicine improvements in privacy and connectivity allow for secure patient consultations, electronic health records (EHRs) are now cloud-based, and some platforms even integrate language translation services, making a digital nomad doctor lifestyle feasible. If you’re a physician considering a digital nomad lifestyle and looking for inspiration, check out Dr. Chelsea Turgeon’s story of practicing telemedicine across 20 countries.
Telemedicine’s Emotional Buffer: Supporting Empathy and Preventing Burnout
While telemedicine allows doctors and patients to connect virtually from anywhere, the physical separation of provider and patient creates an emotional buffer. Some believe this results in less biased decision-making because it allows doctors to focus more clearly on the clinical data and less on the emotional aspects of care, which can eventually lead to compassion fatigue.
Telemedicine platforms now encourage and analyze nonverbal communication during visits. They incorporate tools for maintaining eye contact, reading facial expressions, and providing a “sentiment analysis” through artificial intelligence (AI) technology so that doctors stay connected to their patients’ emotions despite the physical and emotional buffers.
Reduced Compassion Fatigue
Platforms like mend help doctors maintain emotional reserves, reduce burnout, and prepare for longer and more sustainable medical careers—just three benefits of telemedicine for doctors. Each benefit also supports quality patient care, as doctors who practice self-care can better serve those in charge.
Telemedicine platforms include features contributing to reduced compassion fatigue, such as reminders to take breaks, built-in meditation, relaxation exercises, and even sophisticated scheduling or patient self-scheduling that can help a doctor space out or cluster their more emotionally challenging cases, depending on the doctor’s preference. The following table highlights the differences between traditional and telemedicine medical practices.
| Aspect | Traditional Practice | Telemedicine Practice |
| Work Hours | Fixed, often long | Flexible, customizable |
| Patient Interactions | In-person, high emotional involvement | Virtual, potential for emotional distance |
| Work Location | Fixed office or hospital | Anywhere with internet |
| Administrative Tasks | Time-consuming, in-office | Often automated, can be done remotely |
| Stress Levels | Often high due to constant in-person demands | Potentially lower due to flexible scheduling and reduced physical strain |
Technological Empowerment
The technological advancements behind telemedicine are significantly reshaping how doctors provide and how patients receive care. Artificial intelligence (AI) integration in telemedicine has created efficiencies and capabilities that feel more like something from The Jetsons than what you would expect from your primary care doctor. Telemedicine is incorporating and promoting greater access to information and data, which is leading to faster and improved decision-making.
To learn more about the integration of AI in healthcare, explore our article on how AI is revolutionizing patient care.

Source: scientificamerican.com
Artificial Intelligence-Assisted Diagnostics
Telemedicine is increasingly effective: one study of over 35 million records by Epic found that for most telehealth visits across 33 specialties, there was no need for an in-person follow-up visit within 90 days of the telehealth visit. In the cases where follow-up visits were necessary, it was usually for additive care, not duplicative care, which is exactly what it sounds like—care needed in addition to existing care, not a repeat of care already provided. Telemedicine platforms integrate artificial intelligence in many ways, including through pattern recognition algorithms and predictive analytics.
Pattern Recognition Algorithms
Artificial intelligence in telemedicine platforms has started helping doctors improve their approach to early intervention and preventive care, which is contributing to improved patient outcomes. The pattern recognition algorithms in some AI systems can analyze large subsets of patient data and identify new disease correlations that may have been previously overlooked by human analysis. Some of them even offer potential diagnoses for doctor consideration. These algorithms can predict disease progression based on changes to patient data over time, and deep learning models can detect anomalies with high accuracy.
Predictive Analytics
Most industries love predictive analytics, and doctors who use telemedicine are no different. The ability to anticipate healthcare needs before they become more critical is a game-changer that can transform lives. New York’s largest health system, Northwell Health, has been using its in-house, AI-powered solution, iNav, to analyze MRI and CT scan images for cancer, even when those images are taken for unrelated health issues. Northwell has reduced the time to treatment by 50% thanks to this AI technology and is considering licensing it to other hospital systems. Dr. Daniel King said it “totally revolutionized our ability to get these people connected to care.” Some systems can also incorporate genetic data for more personalized health risk assessments.
Economic Paradigm Shift
The business of healthcare is constantly evolving, and telemedicine is evolving right along with it. Market analysis tools powered by artificial intelligence now help doctors meet patients where they are, including underserved populations. Blockchain technology and solutions continue to intrigue and offer capabilities for more secure health records, payments, and more. In addition, new medical models that can benefit doctors financially and increase patient access to healthcare are one of the biggest opportunities in telemedicine.
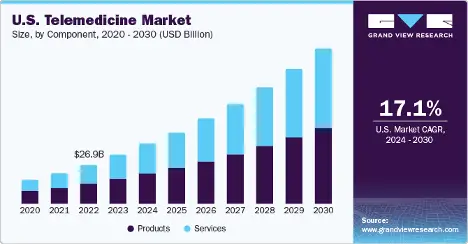
Source: grandviewresearch.com
Micropractice Revolution
The way providers use telemedicine varies far and wide. One movement in healthcare, the “Micropractice Revolution,” encourages quality over quantity. Doctors in this movement are often primary care physicians and provide services through a direct-care model. The idea is that it allows for more autonomy, control, and an opportunity to get to know patients on a deeper level than possible when practicing for a large healthcare company or practice. While this model has pros and cons, such as balancing on-call coverage or managing the administrative burden independently, this concept works with telemedicine. Subscription-based care models and access to the global market are two reasons why.
Subscription-Based Care Models
In subscription-based care models, physicians offer ongoing, personalized care. Patients value this arrangement because their doctor gets to know their medical history and treatment preferences beyond the surface level of their chart. For doctors, a subscription-based care model can provide predictable income and stability. Telemedicine platforms can support subscription-based care models through predictive analytics (useful for setting pricing), automation of tasks, tracking patient engagement, or creating personalized care plans. Examples of subscription-based care models include OurDoctor, HelpCare+, and RemoteMD.
Global Market Access
Another benefit of telemedicine for doctors is access to the global market. One of the organizations at the forefront of telemedicine is WorldClinic. WorldClinic (initially called Voyager Medicine) was founded in 1996 by Dr. Carlin, a former U.S. Navy chief medical officer, with the goal of providing medical care to individuals who live abroad, sometimes in remote locations. Through telemedicine, they now offer real-time consultations and serve travelers and expats all over the world.
Telemedicine platforms often provide multi-lingual support (Vsee Health and LanguageLine, for example), offer currency conversion and international payment processing, and some even inform users of regulatory compliance policies and changes across countries.
Resource Optimization
Some physicians prefer working for a large provider group or insurance company because they don’t want the hassle of setting up their own practice, processes, and operating procedures. However, telemedicine today allows for more efficient use of time and resources, which leads to profitability and improved patient satisfaction. Some telemedicine platforms can handle routine administrative work, appointment scheduling or self-scheduling, and can establish workflows around insurance coding and billing.
Telemedicine systems, such as DocVilla, offer doctors data-driven insights to better manage their practice. Advanced analytics that provides insight into patient demand or staffing needs can elevate the patient experience, and many systems include dashboards to see financial and other metrics in real-time.
Source: ashp.org
The following table highlights some differences between a traditional medical practice and a telemedicine-enabled practice regarding the shifting economic paradigm in healthcare.
| Aspect | Traditional Practice | Telemedicine-Enabled Practice |
| Patient Reach | Local, limited by geography | Global, unlimited by distance |
| Revenue Streams | Primarily in-person visits | Diverse: virtual visits, subscriptions, global consultations |
Ethical Considerations and Professional Growth
As virtual care redefines traditional care boundaries and gives way to telemedicine, physicians must navigate complex ethical questions around patient privacy and security and how to best develop skills to cultivate the physician-patient relationship, such as digital empathy. Ultimately, telemedicine presents an opportunity to enhance ethical awareness and improve patient care.

Source: Canva.com
For a comprehensive overview of telemedicine, including its ethical implications, check out our guide on telehealth and remote medical consultations.
Digital Empathy Development
“Digital empathy” is understanding and sharing another person’s feelings in an online or digital environment. While telemedicine has created an incredible capacity for doctors to connect with patients in new ways and in new spaces, it’s always important to demonstrate empathy—crucial to building trust and improving patient satisfaction and outcomes. The virtual telemedicine environment is one space where doctors may need to develop or adopt new approaches to ensure digital empathy, something more than half of physicians are concerned about.
Telemedicine platforms can provide real-time feedback to the physician about their tone and body language during consultations while also getting a read on patient emotions. More advanced telemedicine systems provide coaching and tips on improving digital empathy skills, sometimes through active listening prompts or pre-scripted phrases such as “I understand your concern.” Virti is an example of an immersive learning platform that can train users on empathy and adaptability, and Empathetics is an example of a curriculum designed for empathy education for physicians.
Non-Verbal Cue Interpretation
When working in a virtual environment, the ability to read patients’ emotions becomes even more critical. Nonverbal cue interpretation is a skill that can lead to patient trust and more accurate diagnosis. Telemedicine offers eye-tracking technology to help doctors maintain appropriate eye contact, analyze micro-expressions, and even provide suggestions for possible reactions to the nonverbal clues a patient provides.
Cultural Competence in Virtual Spaces
Demonstrating cultural competence in virtual settings is as important as in person. Some telemedicine platforms offer real-time cultural context information and translation services, and more advanced systems can provide customized cultural sensitivity training based on a doctor’s patient demographics.
Privacy and Security Innovation
Telemedicine presents unique challenges to privacy and digital security, and physicians who practice through telemedicine platforms should be aware of this. If managed well, it creates an opportunity to build trust with patients through digital security and data protection, which will encourage the use of telemedicine. Blockchain technology and the ongoing discussion of ethical artificial intelligence implementation are two current trends to be aware of.
Source: cacm.acm.org
Blockchain for Medical Records and More
Blockchain technology is already being pioneered in banking and finance, supply chain management, education, real estate, and many other industries. Healthcare is a natural fit, and telemedicine is even more so. Blockchain technology can ensure secure, transparent, and patient-controlled medical records. It can help with care coordination and data fragmentation when a patient has visited multiple providers and can be used for payments and claims. Some believe blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize data management in healthcare completely. Patientory is an example of a blockchain-based platform that allows patients and their providers access to secured data.
Ethical AI Implementation
An ongoing discussion around AI in any industry is ethical AI implementation. Physicians who use or adopt telemedicine platforms will have the opportunity to provide feedback on the tools and AI-generated features. Doctors can share their medical opinions, recommendations, and care decisions, which encourages transparency. This type of information will help guide the implementation of AI in telemedicine.
Learnings Recap
- Telemedicine is redefining professional boundaries, improving work-life integration, emotional well-being, and providing new opportunities to explore one’s passions all over the world while practicing medicine
- Technological advancements in artificial intelligence are reshaping how care is provided and received and leading to enhanced diagnostic capabilities and medical education
- New economic models in telemedicine allow for specialized micropractices and global market access
- Ethical considerations in telemedicine drive innovation in digital empathy and data security
To explore the future of telemedicine and its impact on healthcare delivery, read our article on virtual healthcare in 2025: enhancing accessibility and efficiency.






