Discover what is telemedicine and how it’s transforming healthcare. Learn about telemedicine meaning, services, and its impact on patient care.

The Evolution of Remote Healthcare
What is telemedicine? It’s the practice of providing medical care through digital communication tools. The telemedicine definition is often confused with general telehealth.
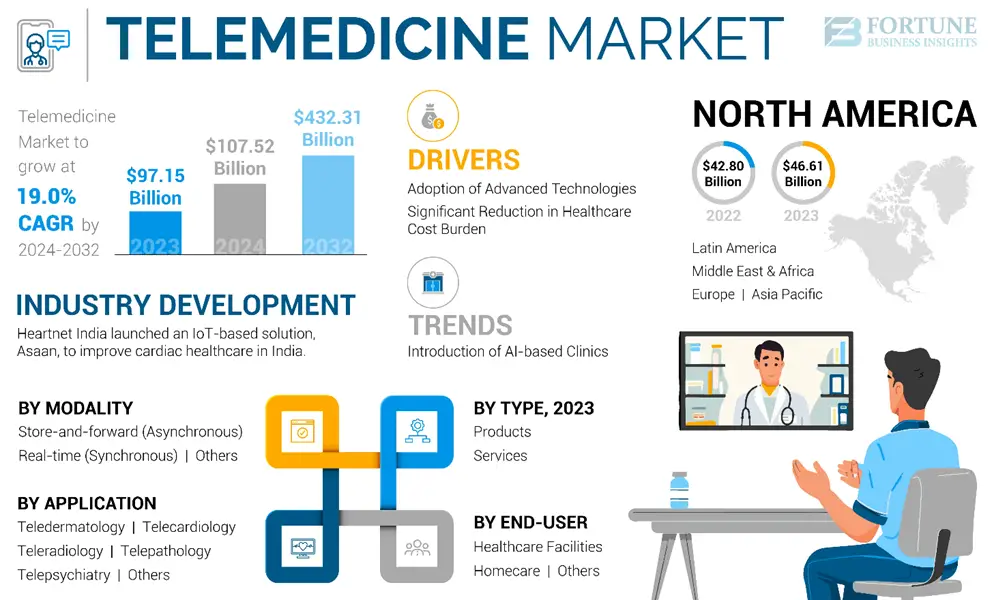
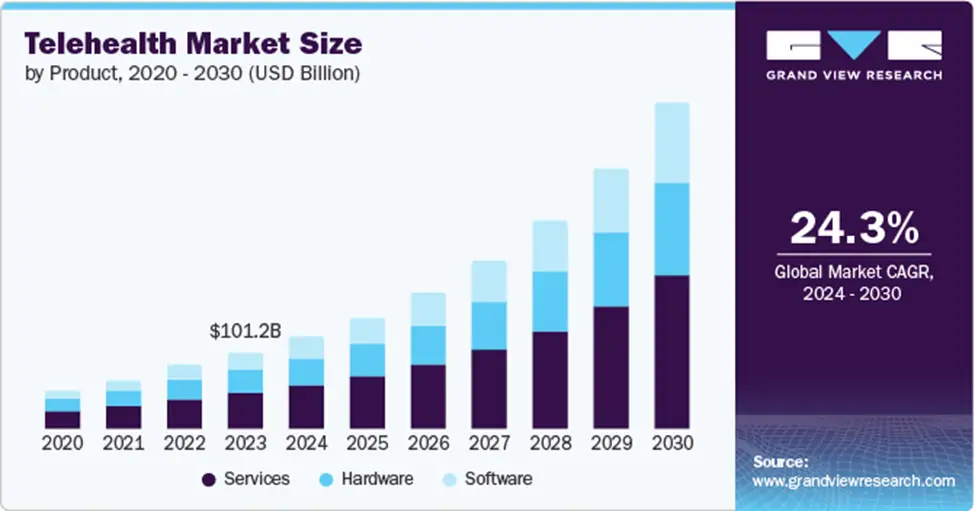
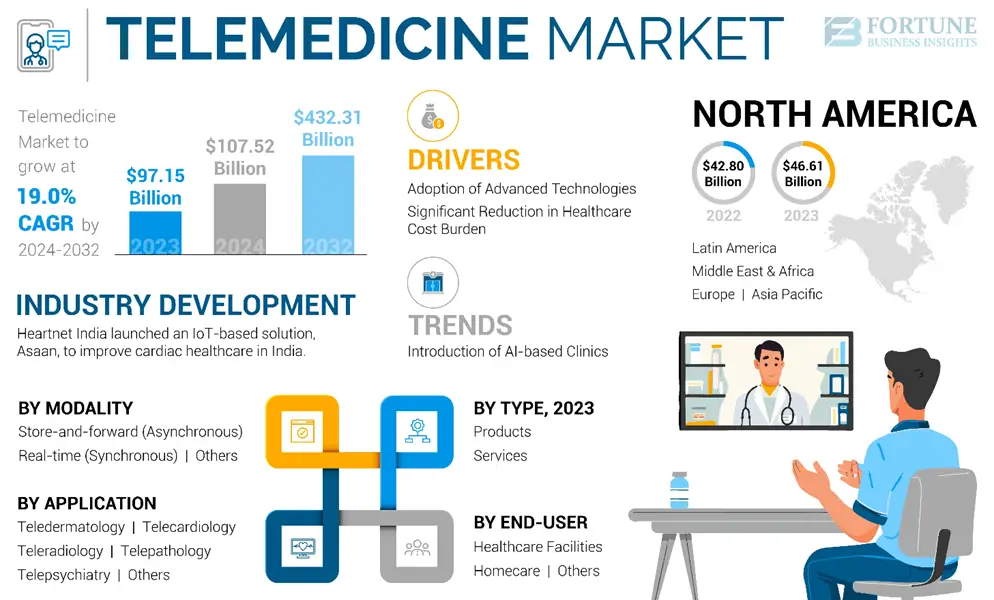
The remote healthcare market was worth $97.15 billion in 2023. It is expected to grow to $432.31 billion by 2032. This means it will grow at a rate of 19% each year. As demand increases, hospitals are expanding telemedicine services, and governments are updating policies to support its growth.
Key Moments in Telemedicine History
- 1876 – Bell patents the telephone, enabling remote communication.
- 1948 – Radiology images are transmitted over telephone lines.
- 1961 – NASA remotely monitors astronaut Alan Shepard’s vitals.
- 1970s – First major remote patient monitoring (RPM) program is launched.
- 1983 – The internet is officially launched worldwide.
- 1999 – Wireless internet and Wi-Fi routers become available.
- 2020 – COVID-19 accelerates telehealth adoption and coverage.
- 2022 – 25% of medical practices offer RPM services.
From Telegraph to Telepresence
Remote healthcare has been around longer than many people think. In the 19th century, doctors used telegraphs to send medical advice to remote patients.
The Space Race’s Contribution
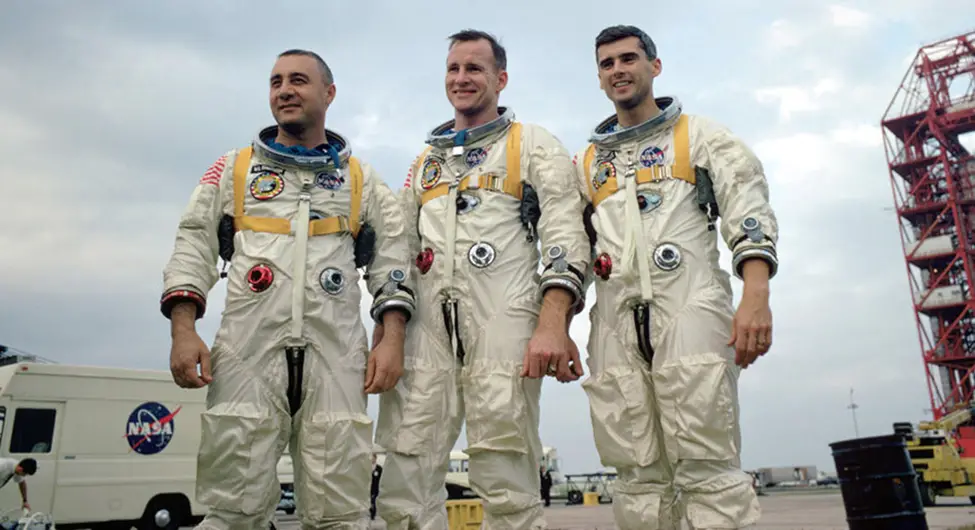

The 1960s Space Race helped answer the question: what is telemedicine? NASA needed a way to check astronauts’ health in space. This need led to remote health tracking systems. These technologies were eventually adapted for military and civilian use, enabling doctors to monitor vital signs from a distance.
Rural Telehealth Pioneers
Rural communities were among the first to benefit from the use of telemedicine consultations on a large scale. In areas with limited access to doctors, technology has made medical care more accessible. Patients can request appointments with some of the best doctors in the world, like those at Johns Hopkins, through the MyChart platform.
The Smartphone Revolution
Smartphones changed the way people access telemedicine services. Patients can now use mobile devices to:
- Schedule telehealth appointments
- Message their doctors
- Track their health data instantly
App-Based Health Ecosystems
Health app systems support virtual visits by creating an easy digital network. This network allows patients and doctors to connect from a distance. Apps integrate with wearable devices, allowing real-time tracking of vital signs like heart rate and blood pressure, which doctors can review during virtual visits. Electronic health record (EHR) apps ensure that patient data is easily accessible across different platforms, improving diagnosis and treatment planning. By connecting telehealth services, pharmacies, and insurance providers, these systems make remote care easier. This helps reduce delays in prescriptions, follow-ups, and medical decisions.
| Provider | Key Features of Health App | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Teladoc Health | 24/7 virtual visits, mental health services, chronic care management | Comprehensive telehealth services |
| Amwell | Integrated with hospitals, supports urgent and primary care | Hospital and clinic partnerships |
| MDLIVE | Affordable on-demand care, therapy, and psychiatry options | Budget-friendly virtual care |
| Hims & Hers Health | Online consultations, prescription services, focus on sexual health and wellness | Accessible and discreet healthcare |
| Zocdoc | Online or in-person doctor booking, video consultations, insurance-friendly | Easy appointment scheduling |
The Nuanced Landscape of Telemedicine Services
Synchronous vs. Asynchronous Care
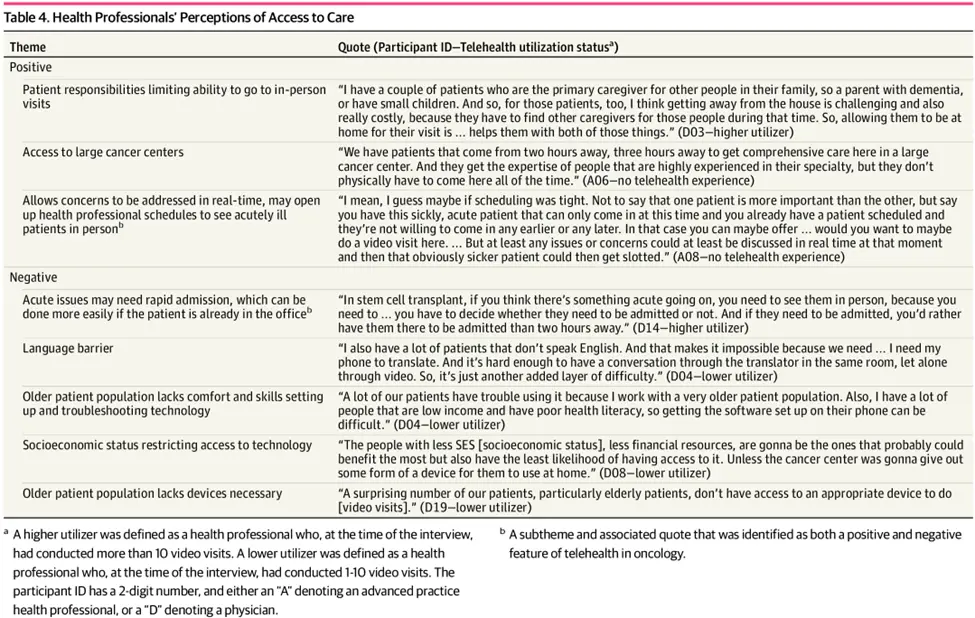
Telemedicine services work in two ways: synchronous (live video calls) and asynchronous (recorded exchanges). Synchronous care allows for real-time interaction. Asynchronous care lets patients send messages, test results, or photos for later review. This is useful for dermatology and prescriptions. Apps or services, like the popular app Nurx, make things easier. They provide medications based on your health information. This helps to reduce wait times, especially for specialized care, like oncology.
A recent JAMA study discusses virtual treatment in cancer care. It also shares important feedback about how doctors feel about remote consultations.
The Art of Virtual Bedside Manner
Telemedicine consultations should feel just as personal as an in-person one. Making eye contact with the camera helps create a real connection, even through a screen. A doctor who listens carefully, repeats key points, and asks follow-up questions shows they are paying attention to concerns.

Clear and simple explanations make it easier to understand diagnoses and treatment plans. A calm and friendly tone can help ease anxiety, and pausing for questions gives time to think and ask anything that isn’t clear. A focused doctor—one without distractions in the background—makes the visit feel more professional and reassuring. These small details help build trust and make virtual care a better experience.
Specialty Telemedicine
Telemed expands access to specialties focused on diagnosis and treatment rather than procedures, including behavioral health, infectious diseases, cardiology, and other cognitive fields.
Teledentistry: Beyond Oral Health
Teledentistry allows patients to send images for expert assessments, reducing unnecessary visits. Platforms like Toothpic and Denteractive connect users with licensed dentists for consultations.
Teledermatology’s Visual Advantage
Teledermatology permits remote diagnosis of skin conditions through photo submissions. AI tools help detect issues early, accurately.
Navigating the Regulatory Maze

Cross-Border Challenges
Laws vary by state and country, making cross-border care complicated. Key issues include:
- Licensing restrictions – Doctors must be licensed where the patient is located.
- Insurance differences – Coverage rules change across regions.
- Prescription limits – Some medications can’t be prescribed across borders.
Licensing Reciprocity Movements
Some efforts are making it easier for doctors to practice across borders:
- Interstate Medical Licensure Compact (IMLC) – Speeds up multi-state licensing for doctors.
- Nurse Licensure Compact (NLC) – Allows nurses to work across states without extra licenses.
Data Privacy in the Digital Health Era
Protecting patient data is paramount. Key concerns include:
- HIPAA (U.S.) & GDPR (Europe) – Laws that set data protection rules.
- Cybersecurity threats – Hackers target telehealth platforms.
- Encryption & authentication – Helps secure patient records.
Blockchain in Telemedicine
Blockchain technology could make apps safer and more efficient:
- Patient-controlled data – Users manage their own health records.
- Improved data sharing – Helps providers securely exchange records.
The Future of Telemedicine: Beyond Video Calls
With telemedicine services expected to grow rapidly, the future looks promising.
Wearable Integration and Continuous Monitoring
Treatment is advancing with wearable telemedicine devices. Smartwatches, biosensors, and implantable monitors help doctors catch problems early. These devices measure key health signs like:
- Heart rate and blood pressure to check cardiovascular health.
- Blood sugar levels for diabetes management.
- Oxygen levels and breathing rates to monitor lung function.
- Activity and sleep patterns to assess overall well-being.
Smart Clothing for Health Tracking
Smart clothing with built-in sensors tracks heart activity, movement, and temperature. As technology advances, these wearables will enhance virtual healthcare.
AI and Machine Learning in Telemedicine
AI is improving the use of telemedicine as it takes over repetitive tasks and helps doctors find health issues, even using robots to assist with remote exams and monitoring. This speeds up care and makes medical help more available. A study from MIT and Brigham and Women’s Hospital was published in JAMA Network Open. It found that patients were comfortable with AI consultations. Boston Dynamics’ Dr. Spot, a robotic system with a telehealth tablet, facilitated remote emergency department visits during COVID-19, showing broad acceptance of AI in healthcare.
Natural Language Processing for Medical Transcription
Natural language processing (NLP) automates transcribing doctor-patient conversations into medical records, improving accuracy and efficiency. It supports multiple languages, enhancing accessibility.
Predictive Analytics for Proactive Care
Predictive analytics helps doctors study a patient’s medical history by wearable device data, analytics can find early warning signs of chronic diseases.
Telehealth vs. Telemedicine: Understanding the Distinction
These two terms are used interchangeably and they are related but not the same.
- Telehealth covers a wide range of remote healthcare services, including virtual visits, health education, and mobile health apps.
- Telemedicine focuses specifically on clinical care, such as diagnosing illnesses and prescribing treatments remotely.
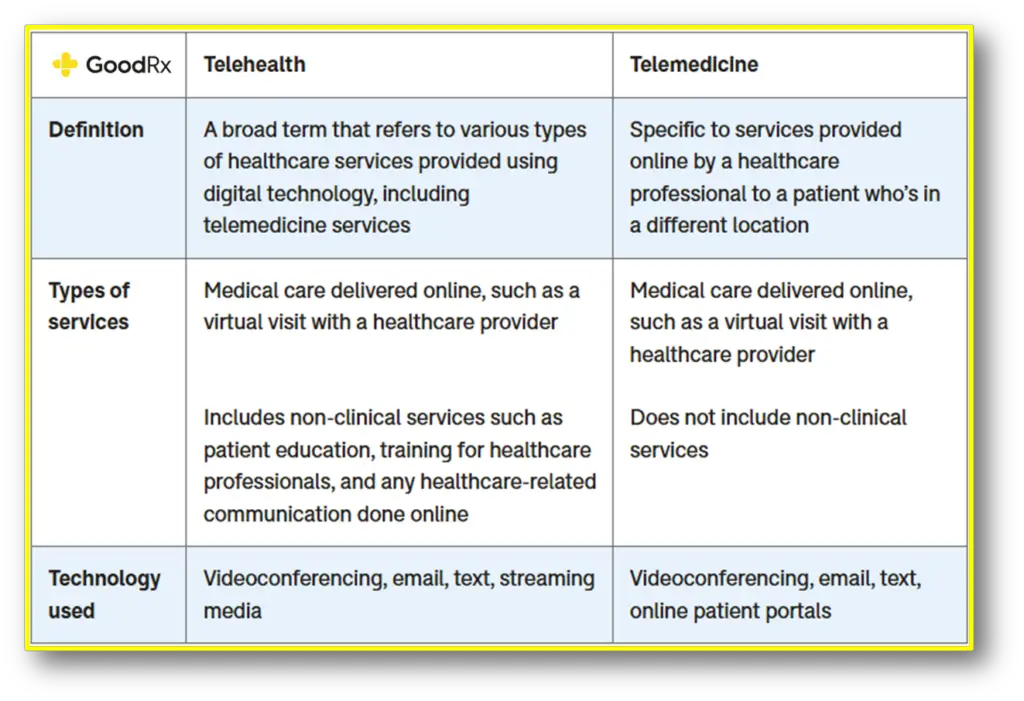
The Broader Scope of Telehealth
Telehealth includes more than just virtual doctor visits. It also covers:
- Live video consultations – Connecting with doctors or therapists in real time.
- Health monitoring tools – Wearable devices tracking heart rate, oxygen levels, or activity.
- Online patient education – Websites and apps that provide health advice and resources.
mHealth: The Mobile Health Revolution
Mobile health (mHealth) uses smartphones, tablets, and wearables to support healthcare. Popular mHealth tools include:
- Fitness apps – Track steps, workouts, and calories.
- Medication reminders – Notify users when to take prescriptions.
- Blood pressure & glucose monitors – Sync with phones for easy tracking.
Telemedicine’s Clinical Focus
- Diagnostic Services – Diagnosing minor illnesses, helping patients monitor chronic disease, or conducting follow-ups.
- Remote diagnosis – Reviewing lab results and scans online.
- Prescription management – Sending medications to pharmacies remotely.
Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM)
RPM allows doctors to track patients’ health from home using smart devices. These include:
- Heart rate monitors – Track irregular rhythms or heart conditions.
- Blood pressure cuffs – Send real-time readings to doctors.
- Glucose sensors – Help manage diabetes more effectively.
The Economic Impact of Telemedicine

Cost-Effectiveness for Patients
Patients save money in several ways such as:
- Lower consultation fees – Virtual visits cost significantly less than in-person.
- Eliminates travel costs – No need to pay for gas, public transportation, or parking.
- Reduces missed work hours – Patients can attend appointments without taking time off.
Virtual Urgent Care Savings
Urgent care centers are expensive, but with apps, patients can book same-day doctor’s appointments and urgent care visits at a lower cost.
- Average cost of in-person urgent care – Between $150 and $250 per visit.
- Typical virtual consultation fee – Usually ranges from $40 to $75.
Provider Efficiency and Revenue Streams
Remote care helps healthcare providers maximize their time and increase earnings by offering flexible care models.
- Shorter visit durations – Virtual appointments are often 10–15 minutes long.
- Higher daily patient volume – Physicians can consult with more patients in less time.
- Additional revenue streams – Subscription-based telehealth services and remote monitoring programs.
Telemedicine as a Competitive Advantage
Hospitals, clinics, and private practices that embrace remote access care gain a strategic edge in the healthcare market.
- Improves patient retention – Keeps patients engaged long-term, many individuals prefer digital healthcare.
- Supports specialized services –Allows remote consultations with experts in different fields.
Overcoming Barriers to Adoption
Technological Infrastructure and Digital Divide
Barriers must be overcome for better access to healthcare across America. Rural Medicare patients increasingly used virtual visits, with those managing serious mental illnesses, like bipolar disorder, making up a significant portion.
A 2021 JAMA study, Trends in Outpatient Telemedicine Among Rural Medicare Beneficiaries (2010-2019), highlights remote health technology growth over the decade. In some areas, over 10% of beneficiaries relied on this method each year. A study chart illustrates this steady rise.
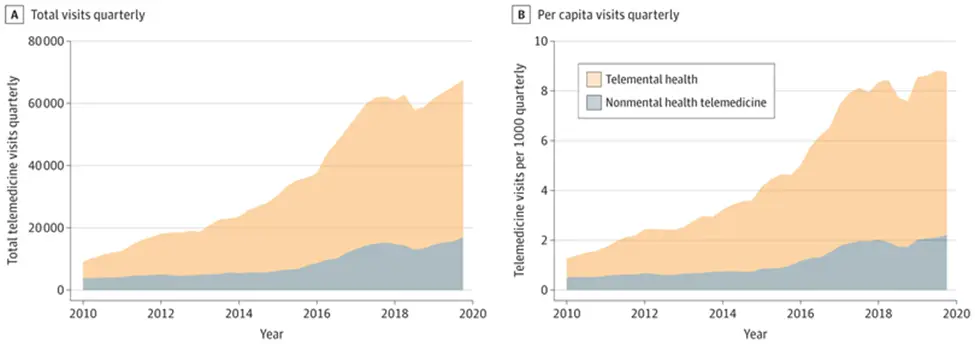
5G and Accessibility
5G technology helps address connectivity issues for telemedicine devices by:
- Enabling smoother video calls and real-time health tracking.
- Expanding patient care in remote and underserved areas.
Cultural and Generational Acceptance
While the use of digital health is growing, some people remain hesitant due to:
- A preference for in-person visits, particularly for complex care.
- Challenges among older adults in using digital apps.
Telemedicine Literacy Programs
Medical literacy programs provide can provide essential training for patients and caregivers from afar. These include:
- Booking virtual appointments and using health apps.
- Step-by-step guides and hands-on training to boost confidence.
Learning Recaps
Bottom line—telemedicine has transformed healthcare by making it more accessible, affordable, and efficient. Patients can connect with providers from anywhere, reducing barriers to treatment and cutting costs. Advances in AI and wearable technology continue to improve remote diagnostics and monitoring, ensuring high-quality care beyond traditional settings. As digital health evolves, its role in modern medicine will only grow stronger.